emerging-mind.org
eJournal ISSN 2567-6466
(info@emerging-mind.org)
Author: Gerd Doeben-Henisch
gerd@doeben-henisch.de
Abstract
Part 4 was the first Milestone. For details see that document. In part 5 only small modifications and extensions happened.
Modifying Control Window Calls
There is only one simple call to start the control window without any other functions, this is ctrlWinStart(). All other calls do operate on features of the control window.
Extending Control Options With Percentage of Objects
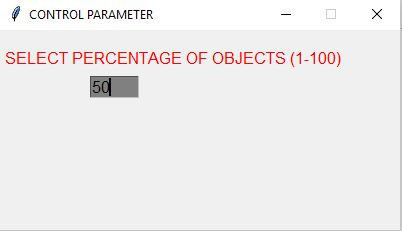
A new control feature has been introduced: asking for the percentage of objects to be placed in the environment: ctrlWinLocateAct(winC). This allows a number between 1-100. The percentage of food-objects is still kept fixed with ’nfood = 1′.
The Whole Story Now
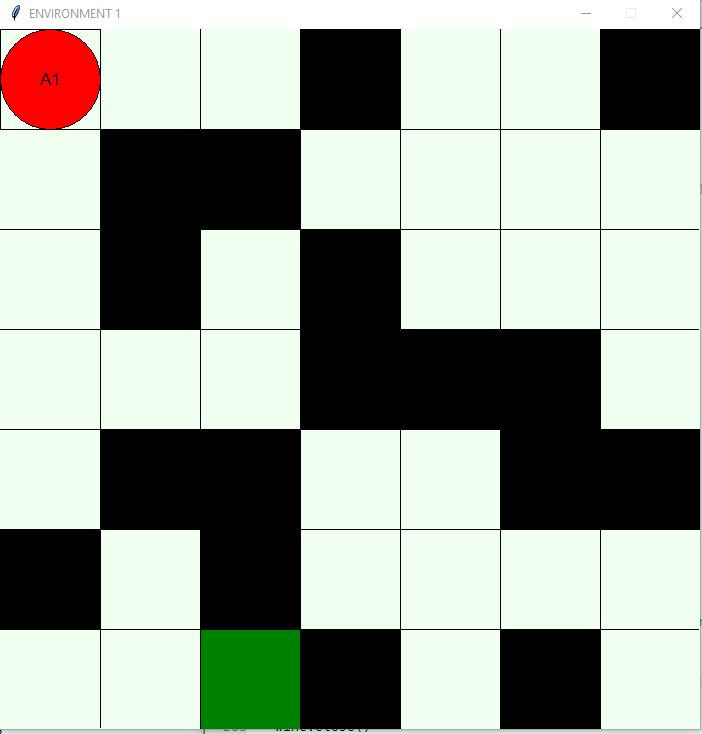
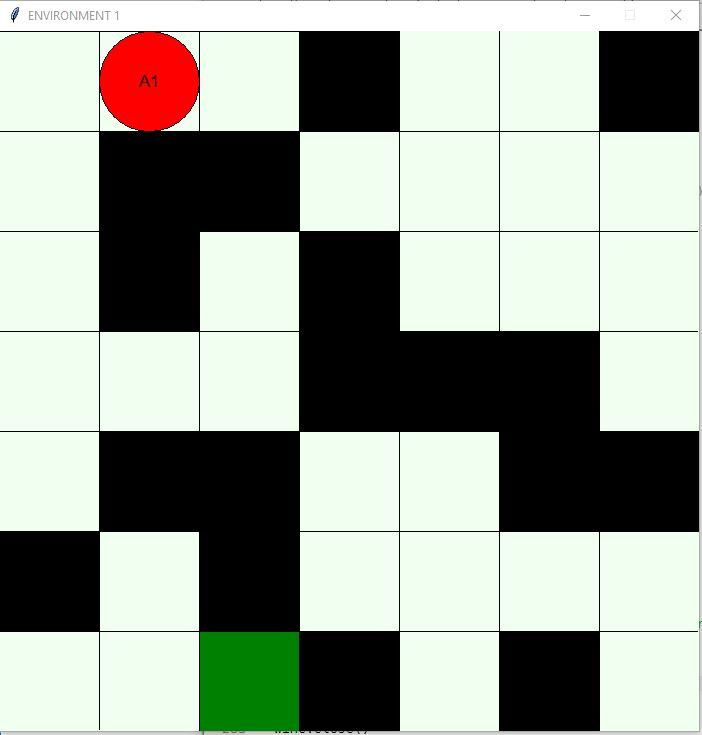
- A 7 x 7 grid is offered with empty cells.
- The user is asked for the percentage of objects in the environment (nobj) which shall randomly be distributed (black cells).
- 1% of cells is randomly occupied by food (i.e. here one cell) (green cell).
- The start position of an actor (red circle) can be selected by pointing into the grid.
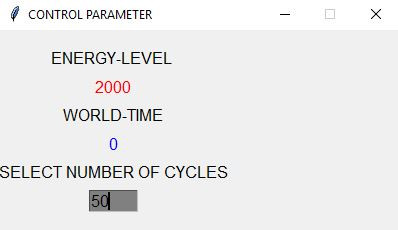
- The number of cycles can be entered how often the environment shall be repeat the event loop.
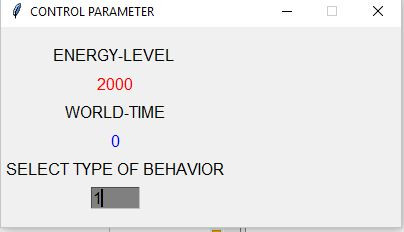
- The type of behavior function of the actor can be selected: manually (:= 0), fixed (:= 1) as well as random (:= 2). With option 1 or 2 the demo is running by its own. With option 0 you have to select the next direction manually by clicking into the grid.
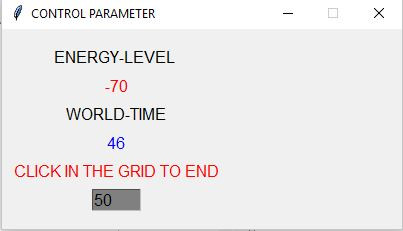
- While the demo is running it reports the actual energy level of the actor as well as the actual ‚Time of the environment‘ (which corresponds closely to the number of cycles).
- If either the maximum number of cycles is reached or the energy of the actor is below 0 the application will stop and after clicking into the grid vanishes from the screen.
Asking for Percentage of Objects
Asking for Number of Cycles
ASKING FOR POINTING INTO THE GRID TO LOCATE ACTOR

Showing Env With Obstacles and Food
Select Behavior Type
Final Stage
The Importance of Freedom and Creativity
Although this environment is very simple, it can demonstrate a lot of basic ‚verities‘. It shows directly the inappropriateness of a fixed behavior even in a static environment. This implies that a non-fixed behavior realized as a random behavior is in principle strong enough to find a solution (if there is any). Whether a solution is possible or not depends from the available time which in turn depends form the available energy.
If one interprets‚random behavior‘ as a behavior based on freedom and creativity then one has here a strong motivation that a society based on freedomand creativityhas (other ‚bad‘ factors neutralized) the best chances to master an unknown future.
How to Continue
You can continue with Part 1 ‚How to Program with Python under ubuntu 14.04?‘